Can a Dehumidifier Make a Room Cooler
The dehumidifier doesn’t cool the room Temperature. Rather, it can raise the temperature by one more degree. It is used to reduce the moisture in the room. There are two kinds of dehumidifiers, refrigerant type and desiccant type dehumidifier. Refrigerant-type dehumidifiers are very common and used in areas like homes, garages, offices, etc. It runs based on the refrigeration cycle, which is similar to the air-conditioner. That’s why many people get confused about whether it can cool the room temperature or not. Dehumidifiers are made for those areas which have high moisture levels in the air. So that the moisture level can be reduced, It has nothing to do with cooling the air. It wasn’t created for cooling. In this blog I will explain this whole thing and also the working process.
In desiccant-type dehumidifiers, there is silicon gel in the desiccant rotor inside the dehumidifier. The moisture (H2O) in the air gets absorbed by the silicon gel because they both are non-polar. So there is no way a desiccant dehumidifier can cool your room.

Air-conditioner & refrigerant type dehumidifiers run with the same refrigeration system. Because of that, they share a lot of commonalities between them, like the air conditioner works like a dehumidifier and they also have drain pipe line in the air-conditioner. Air conditioner absorbs very little moisture from your room temp compared to the dehumidifier. But dehumidifiers can’t cool room temperature because the internal component setup is different and for that reason, they work differently. Let’s talk about how they work and why dehumidifiers can’t cool room temp.
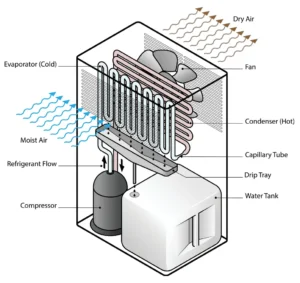
In the dehumidifier evaporator and condenser are installed side by side. Moist air first comes to the cold evaporator, evaporator absorbs the moisture from the air. During this process, this air gets cold and this cold air goes to the hot condenser where it turns back to normal temperature or it can raise the temperature by one more degree.
But in an air conditioner, there are 2 units called an indoor unit and an outdoor unit. The evaporator is installed in the indoor unit which cools the indoor air and during this process, the refrigerant gas gets heated. This hot refrigerant gas goes to the outdoor unit where the condenser makes it cool again and sends it to the indoor unit so that the cooling process can continuously run. That’s the difference between both of them. Below I am explaining how the dehumidifier and the air-conditioner work.
Dehumidifier:

If you take a bottle of cold water out from the fridge, you will notice that water droplets are formed outside the bottle. The reason behind this is because the coldness of the bottle causes a heat exchange with the surrounding air. As we know, there’s moisture (H2O molecules) in our surrounding air and when it loses heat during this heat exchange with cold surfaces like your water bottle, it becomes heavier and condenses forming water droplets on the bottle.

Dehumidifiers work exactly that way. In a dehumidifier, they have an evaporator unit, a condenser unit, a compressor and also a blower fan as 1 whole unit while for air conditioner they are split into two units. They have an indoor unit and an outdoor unit where both these units parts are responsible for cooling too but in general internal parts, such as the evaporator belong to the indoor unit. while the compressor, condenser and expansion valve belong to the outdoor unit. Those are internal parts-wise differences between air conditioners and dehumidifiers.
In refrigerant dehumidifiers, the liquid refrigerant is chilled and flows to the evaporator, as we know the child refrigerant flows through the Evaporator, and because of that evaporator temperature is much lower than room air. There is a blower fan before the evaporator and condenser that sucks room air into the dehumidifier.
When this room air comes to the evaporator, heat exchange happens between the warm room air and the cold refrigerant in the evaporator. The evaporator absorbs heat from the room air, and because of heat exchanges the liquid refrigerant turns into a gas. At this point, the room air loses heat & the moisture in the air becomes heavier and sticks to the evaporator, This is how in the Evaporator room air is dehumidified.
The refrigerant is now in a low-pressure hot gaseous state. This low-pressure refrigerant gas goes into the compressor, In compressor this low pressure gas get compressed and turns into high-pressure superheated gas.
This high-pressure, superheated refrigerant gas then flows to the condenser, where it loses heat and returns to its liquid state. The cold liquid refrigerant gas expands by an expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and sends it back to the evaporator, This is how this process constantly runs.
In the beginning, I explained why water collects on the outside of a cold water bottle. The evaporator works in the same way. In a refrigerant dehumidifier, the evaporator and condenser are positioned side by side. When the blower fan pulls room air into the evaporator and the evaporator removes moisture, the air becomes cold. This cold air then moves directly to the condenser, which is located just behind the evaporator. The cold, dehumidified air absorbs heat from the condenser, bringing it back to room temperature before being released back into the room. Through this heat exchange process, the dehumidified air is returned to the room at a normal temperature. The water collected inside the dehumidifier is drained out through a pipe.
Air-conditioner:
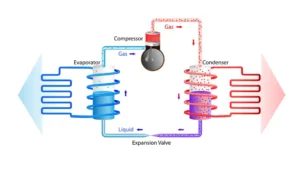
Air conditioner has two parts, one is indoor unit and other one is outdoor unit. Evaporator, blower fan, EEV (Electronic Expansion Valve), those are the parts of indoor unit. And compressor, condenser, blower fan, expansion valve are part of the outdoor unit.
In this process, chilled liquid refrigerant from the outdoor unit enters the evaporator. During this time, the blower fan inhaled room air around the evaporator. In the evaporator, the chilled liquid refrigerant absorbs heat from the room air through heat exchange, because of that room air get cold. After absorbing the heat, the liquid refrigerant converts into gas, which flows through copper pipes to the compressor. The compressor compresses this low-pressure gas, turning it into superheated high-pressure gas.
This high-pressure gas then flows to the condenser. The blower fan directs high-speed air across the condenser pipes to absorb the refrigerant’s heat. In the condenser, the superheated gas cools and then passes through an expansion valve, which expands the cooled refrigerant, turning it into liquid form. This liquid refrigerant flows to the evaporator and that’s how air conditioning system works.

