
What Size Dehumidifier Do You Need? Complete Capacity Guide
You will need permeation load, load through the door, and population load—these three data points—to know which CFM dehumidifier you need to select based on your place. First, we will explain a bit about it, then we will show a practical example of the calculation. Also, I have attached my air PDF as study material.
In winter, the maximum moisture level can be 60%, and in summer, the minimum moisture level can be 35%. If moisture becomes more or less than this limit, then it is not good for the human body.
If your place has a boiler or chilled water system, then you can easily maintain a 50–60% moisture level. In reality, during cooling load calculation, we can reduce the moisture level lower than this, but that would cause issues for work. That is why, with the existing chilled water system, we maintain 55–60% moisture. When the requirement is less than 55%, we should go for a desiccant dehumidifier. The best option will be to use the dehumidifier in combination with an existing AHU
Let’s see a practical calculation for a dry food production factory:
Permeation load:
Permeation load is how much moisture is coming to your place through your wall. To get this information, you need to collect below data from the client to get the permeation load,
- Area of the place – 60′ x 42′ x 16′
- Outside dry bulb temperature & wet bulb temperature – 95 F dbt*; 75 F wbt*
- Inside dry bulb temperature & wet bulb temperature requirement – 75 F dbt; 35 percent rh
- Door size, quantity and how many times they will open in an hour – 1 door (6′ x 7′); opened 6/hr
- Number of people working in area – 10
- Construction (type of wall) – 8″ masonry
- Make-up air/ Fresh air specified by owner – 350 cfm.
Now apply this data to this formula,
V/C × ∆G × F1 × F2 × F3 × F4 = Grains per hour.
V = 60 × 42 × 16 = 40,320 ft.3
C = 14 (Conversion constant / Specific volume of dry air @ 95°F)
∆G = 75 (Apply inside and outside temperature on the psychometric chart, this is how you can get the data, 121 – 46 = 75 grs/lb.)
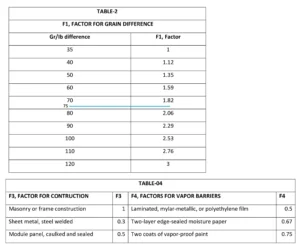
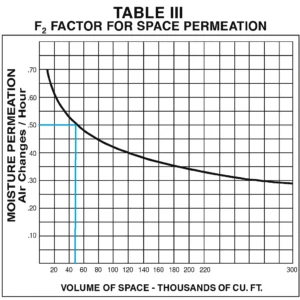
F1, F2, F3, F4 are factors, collects this data from below tables,
F1 = 1.94 (From Table II – Factor for moisture difference of 75 gr/lb – interpolated)
F2 = 0.5 (from Table III)
F3 = 1.0 (From Table IV – Factor for 8” masonry)
F4 = .75 (From Table IV – Factor for 2 coats paint)
As you can see we have got all the data to apply in this formula.
40,320/14× 75 × 1.94 × .5 × 1.0 × .75 = 157,140 grs/hr
Permeation load is 157,140 grs/hr.
Load Through the door:
Every time you open the door or window, moisture can come inside. So, here we will calculate if a door opens 6 times an hour, how much moisture can come inside. To calculate this, you will need below data:
- A= Area of the door (6*7 = 42 sqft)
- Ohr = 6 (door will open 6 times in an hour)
- C = 7 (Conversion constant)
- ∆G = 75 (we find this from the permeation load)
- F1 = 1.94 (we find this from the permeation load)
Let’s apply this data to the formula below,
Ohr × A/C× ∆G × F1 = grs/hr
6 ×42/7× 75 × 1.94 = 5,238 gr/hr
So, the door load is 5238 gr/hr.
Population load:
As you know, moisture can come from the human body. In winter, our body gets dry because dry air absorbs moisture from our body. Here we will calculate how much moisture can be released from 10 people in a production place. To complete this information, you need to know the population of the space. Then see the table below:
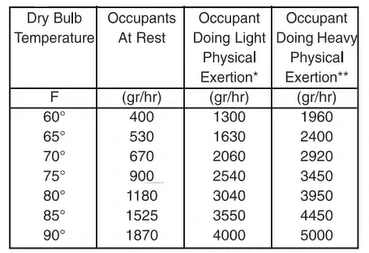
Imagine the population number is 10, and we already know that the ∆G = 75. SO, remember that if it were a gym, then we would choose 3450, or any space where people don’t have any significant physical work, then we would choose 900. But as you know, it is a production space; for that reason, we chose 2540 gr/hr.
Now multiply the population number by 2540, and you will get the number.
2540*10 = 25400 gr/hr.
So, the population load is 25400 gr/hr.
Total load:
157,140 grs/hr Permeation
5,238 grs/hr Through door
25,400 grs/hr Population load
187,778 grs/hr Total
Now process with the following calculation:
X = C × (gr/hr÷60)÷ (S – G)
X = cfm Delivery air rate from dryer to space
gr/hr = total grains per hour in space
C = 14 = constant
S = 46 Grs/lb (how much moisture you need inside the moisture, this is user data.)
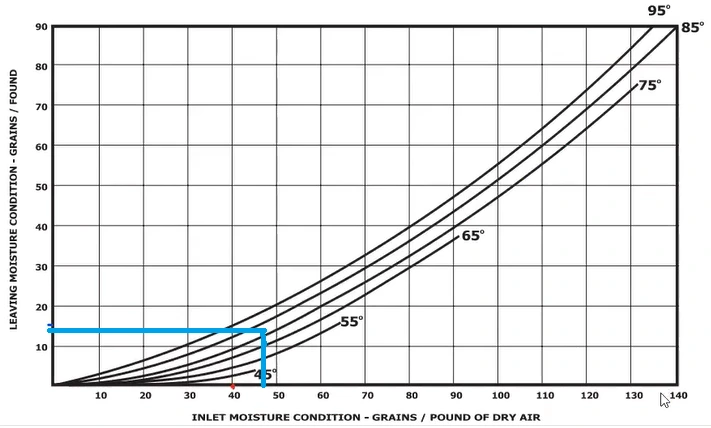
G = 14 Grs/lb (As you can see, S = 46, apply this on the graph and you will find the answer is 14)
Let’s apply all the data on this formula:
X = C × (gr/hr÷60)÷ (S – G)
14 x (187778÷60) ÷ (46-14) = 1369 CFM
So, for the production space you will need a 1369 CFM dehumidifier.
I hope things are clear now for you. If you still have any problem regarding the dehumidifier capacity & size calculation,
Read this Bry air PDF, you will find a lot of more examples and study materials here.
PDF Link: BryAir(aircondiary.com) Dehumidifier Calculation-Sheet
